PRINCIPLE OF WEB FORMATION IN A SIMPLE AIR LAYING PROCESS:
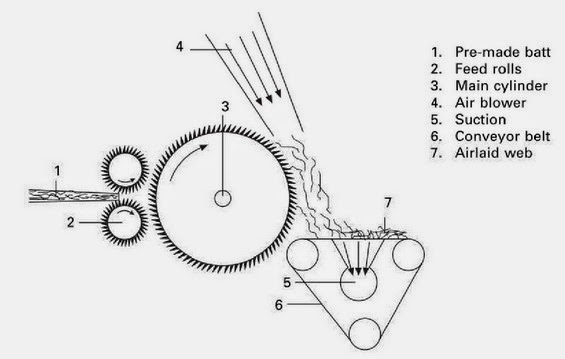
- Natural or man-made textile fibre (cut length >25 mm)
- Short cut fibres (generally <25 mm)
- Wood pulp (1.5–6 mm)
- The fibers are oriented randomly on the fabric surface – isotropic structure.
- Voluminious webs can be produced
- The range of the area weight is wider (15 – 250 g/m2) but the mass uniformity of light air laid (up to 30 g/m2) is bad.
- Wide variety of processable fibers
- Low level of opening fiber material by lickerin roller Thus is suitable to use pre-opened fibers or combine air laid with card machine – Random card machine.
- Variable structures of web in width of layer due to irregular air flow close to walls of duct . This problem requires high quality design of duct.
- Possible entangling of fibers in air stream. This problem can be reduced by increasing the ratio air/fibers which nevertheless means decrease in performance and increase of energy consumption due to high volume of flowing air.
QA = K.P.L2/D
Thus is suitable to use short fibers for this technology.
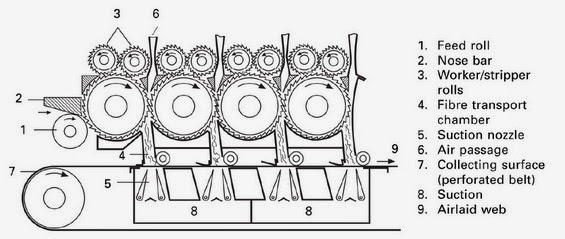
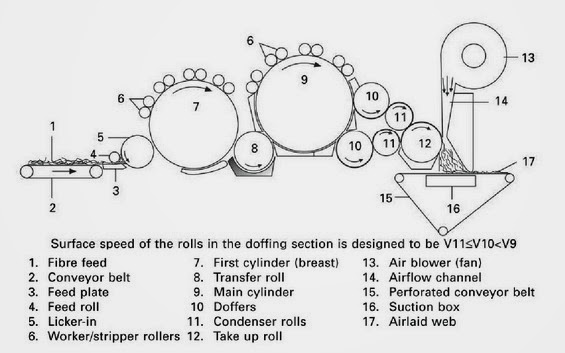
Random cards – combination of air laid and carding technology:
A major objective of this combination is isotropic textile fabric (random orientation of fibers) with good mass uniformity of light fabrics and with high production speed. - The first part – card machine opens perfectly fibrous material so single fibers are as a output.
- The second part – air laid system uses the centrifugal force to strip the fibers off a roller and. put them down on an air controlled scrim belt.
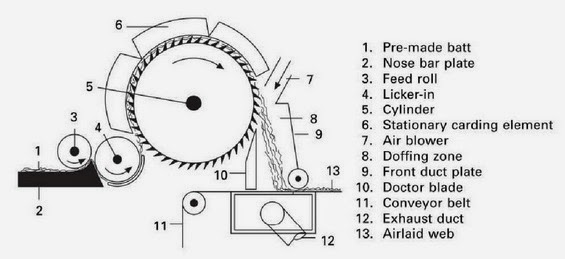
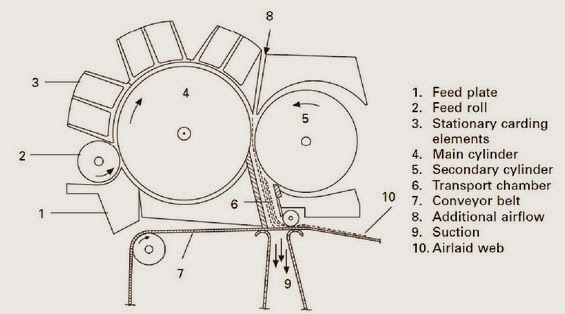
MAIN VARIATIONS OF RANDOM CARDS:
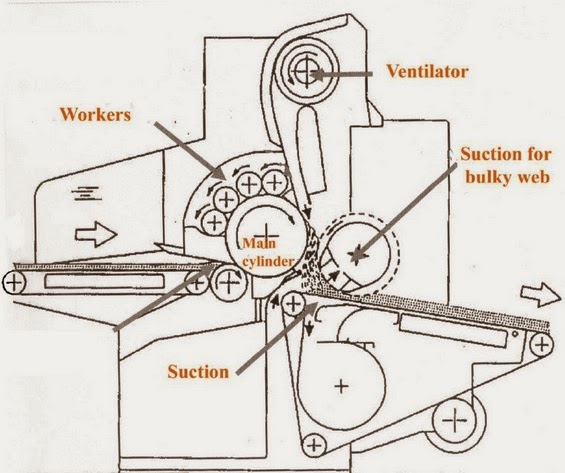
AIR LAID AND RANDOM CARDS: USED FIBERS:
Synthetic fibres, viscose, cotton and blends thereof; natural fibres such as flax, hemp, sisal etc.; Reclaimed textile waste and shoddy, cellulose pulp 1.7 - 2000dtex. Max. 120 mm staple length
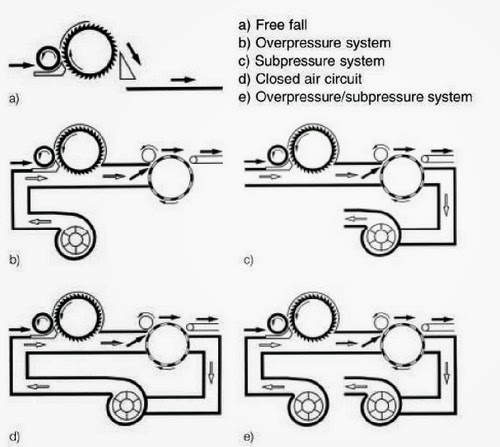
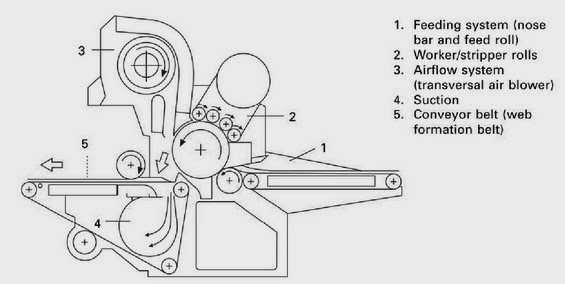
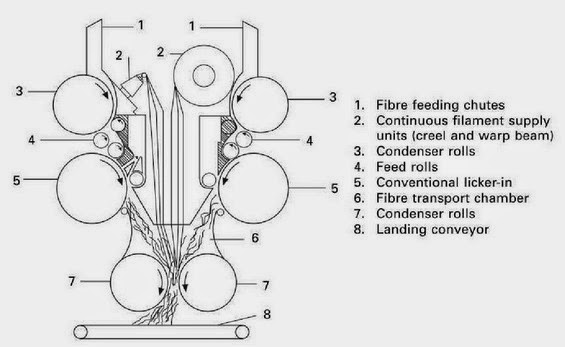
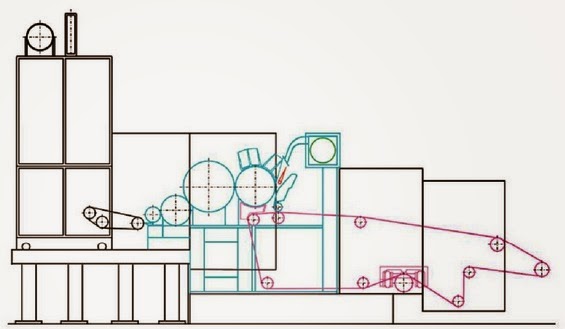
FEEDING SYSTEM OF RANDO WEBBER:
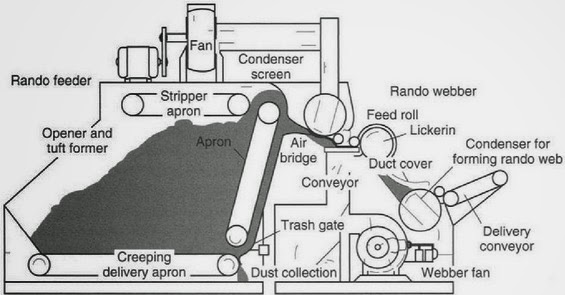
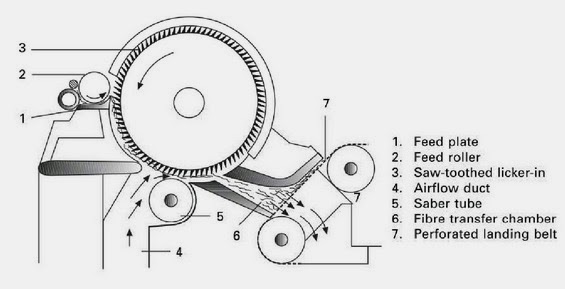
RANDO-WEBBER SYSTEMS WITH PERFORATED SCREEN:
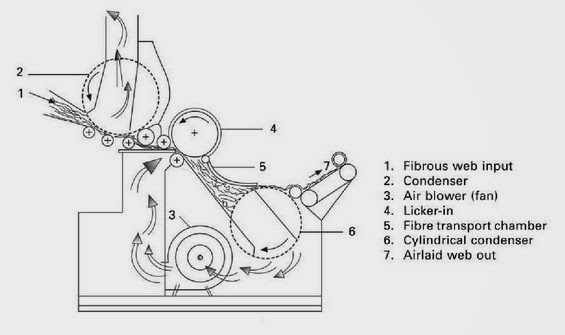
RANDO-WEBBER SYSTEMS WITH CYLINDRICAL CONDENSERS:
- Relatively narrow widths up to about two metres
- Webs of 10– 3000 g/m 2
- Virgin or recycled fibres
- Filtration, home furnishings, automotive fabrics, insulation and some medical specialities
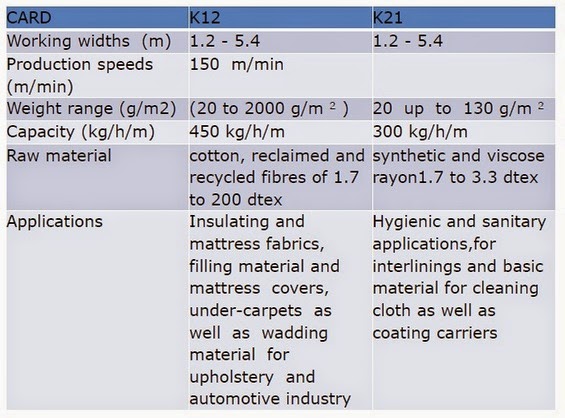
- K12 is more particularly suited to coarse fibres (10–110 dtex), Basic weight range 20– 2000 g/m 2
- K21 is more particularly suited to synthetic and viscose rayon fibers of (1.7–3.3 dtex), Basic weight range 10–100 g/m 2
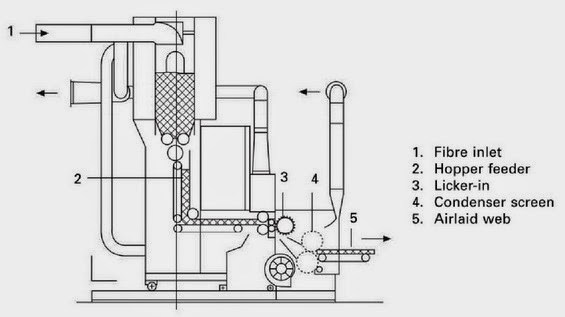
- Air velocity ( 140 m/s)
- Surface speed of the cylinder ( 20–60 m/s)
- Staple fibres ranging from 13–75 mm
- Typical MD/CD ratio of 1.2–1.5:1
- Production rate of 200–260 kg/h/m
- Web weights of 35–200 g/m 2
- Fibre types cotton, viscose rayon, PET, PP, PA
- Fibre length of 10–40 mm.
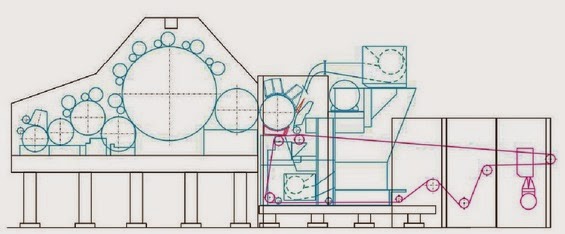
- The turbo-unit TU is either fed by pre-carded webs via a feed plate intake or may be combined with a random card.
- The turbo-roll is equipped with carding segments.
- Aerodynamical web-forming by centrifugal force, doffer fan and suction conveyor
- Lower to medium fibre fineness range
- Staple length: approx. 10 - 80 mm
- Web weight: approx. 25 - 450 g/m 2
- Throughput depending on fibre fineness and fibre type: up to approx. 400 kg/h/m of working width
- Working widths: up to 4.000 mm
- Web speed: approx. 20 - 120 m/min
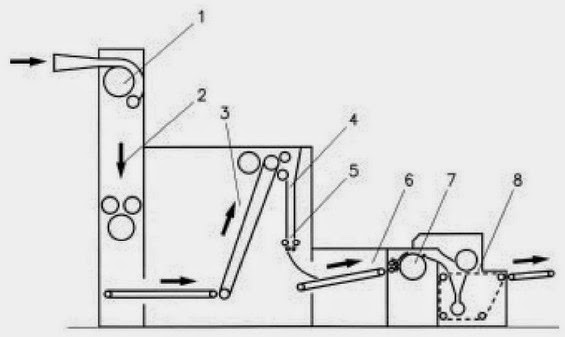
- Web weight ranges from 300 to 3000 g/m 2
- Production speed of up to 10–15 m/min
- Fibre length should be in the range 20–75 mm
- Cotton, man-made, glass fibres
- Hemp, flax, sisal, coconut
- Bed covers, mats, upholstery and insulation material, carrier material for carpets, industrial and geotextiles as well as furniture textiles
- HIGH ISOTROPICITY
- HIGH LOFT (IF REQUIRED)
- HIGH POROSITY (95–>99%)
- HIGH ABSORBENCY AND WICKING RATE
- SOFT HANDLE
- ADEQUATE TENSILE STRENGTH
- GOOD RESILIENCY (COMPRESSION RECOVERY)
- HIGH THERMAL RESISTANCE.
- Chemical bonding: napkins, table cloths and wipes
- Thermal bonding: nappies (different components, i.e., acquisition layer, distribution layer and absorption core), feminine hygiene/incontinence products and insulation
- Spunlacing: wet and dry wipes for domestic and industrial applications medical textiles (including disposable gowns, curtains, wound-care dressings, bed sheets), filtration media
- Needle punching: interlinings and shoe linings, wadding, medical and hygiene products, geotextiles and roofing felts, insulation felts, automotive components, filters, wipes
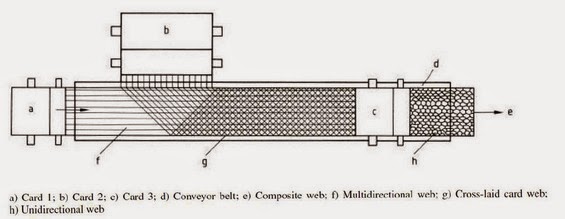
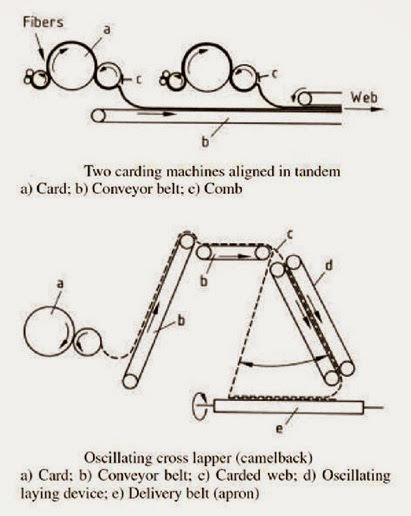
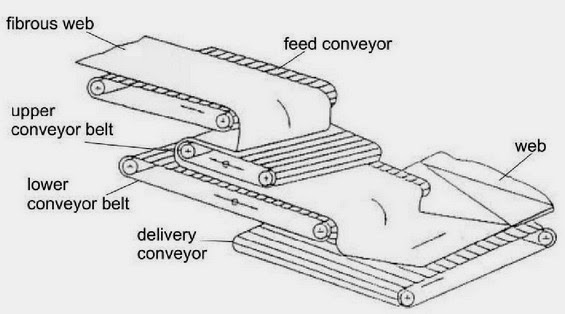
- Increasing the web mass
- Increasing the web width
- Determining the web strength in the length and cross directions
- Improving the end product quality
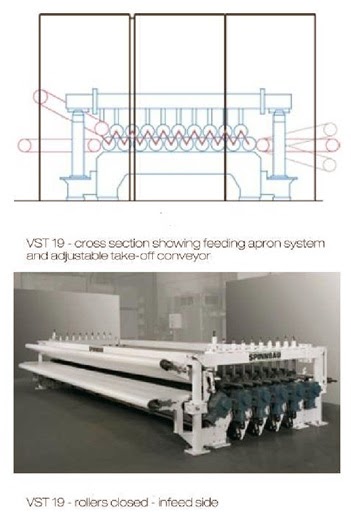
MERITS AND LIMITATIONS OF CARD – CROSS LAPPING AND AIR LAYING:
 |



 06:31
06:31
 vishnu
vishnu

 Posted in:
Posted in: 

.jpg)





0 comments:
Post a Comment